(Automated save: adding PEC_Migrated template.) |
(Update with the copy of version: draft) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
{{Template:PEC_Migrated}} | {{Template:PEC_Migrated}} | ||
| + | Use the '''Bot''' block when you want to use a chatbot resource in your application. | ||
| − | + | Chatbots are software applications that apply automatic speech recognition and natural language understanding to listen and respond to customers in a way that resembles a conversation with a live agent. They have an advantage over [[SpeechGrammarsBar|Speech Grammars]] in that they are able to "learn" from each interaction, which means they are always improving their ability to figure out what a customer wants to do without needing that person to provide specific phrases or commands. | |
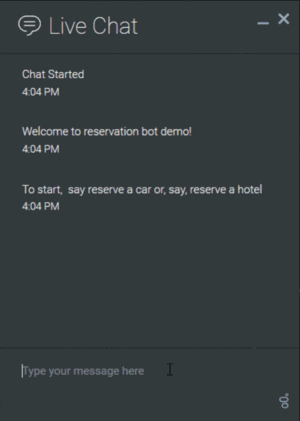
For example, they can ask questions and collect information from a customer about setting up a reservation: | For example, they can ask questions and collect information from a customer about setting up a reservation: | ||
| − | [[File:chat_demo.gif| | + | [[File:chat_demo.gif|none|thumb|Click to view larger]] |
| − | Designer bot resources are managed from the [[SpeechGrammarsBar#Bot_Registry|Bot Registry]], where you can | + | Designer bot resources are managed from the [[SpeechGrammarsBar#Bot_Registry|Bot Registry]], where you can add and manage bot resources from your bot services provider (for a list of supported providers and details about adding bot resources to Designer, see the [[SpeechGrammarsBar#Bot_Registry|Bot Registry]] page). You can use multiple bots in an application, from any of the supported bot services providers. |
| − | + | Typically, you would add a '''Bot''' block to the '''Self Service''' phase of your application. You can then customize the application logic to specify additional handling, such as call a '''Shared Module''' for managing a specific type of intent or send the customer to a live agent for more assistance. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | == Intents and Slots tab == | |
| − | Use the settings in the '''Configure Bot details''' section to select the '''provider''' and '''name''' of the [[SpeechGrammarsBar#Bot_Registry|bot resource]] you want to use. Designer then automatically populates the block properties with '''Intents and Slots''' | + | Use the settings in the '''Configure Bot details''' section to select the '''provider''' and '''name''' of the [[SpeechGrammarsBar#Bot_Registry|bot resource]] you want to use. |
| + | |||
| + | Designer then retrieves the details for your bot from the bot services provider and automatically populates the block properties with '''Intents and Slots'''. For each Intent, Designer automatically creates an associated child block (similar to how the [[Menu|Menu block]] creates child blocks for each menu option). | ||
In the '''Intents and Slots assignment''' section, you can select the variable that holds the '''Intent''' (what does the customer want to do?) and values for the '''Slots'''. The '''Slots''' (or ''entities'') help provide additional context to the intent. | In the '''Intents and Slots assignment''' section, you can select the variable that holds the '''Intent''' (what does the customer want to do?) and values for the '''Slots'''. The '''Slots''' (or ''entities'') help provide additional context to the intent. | ||
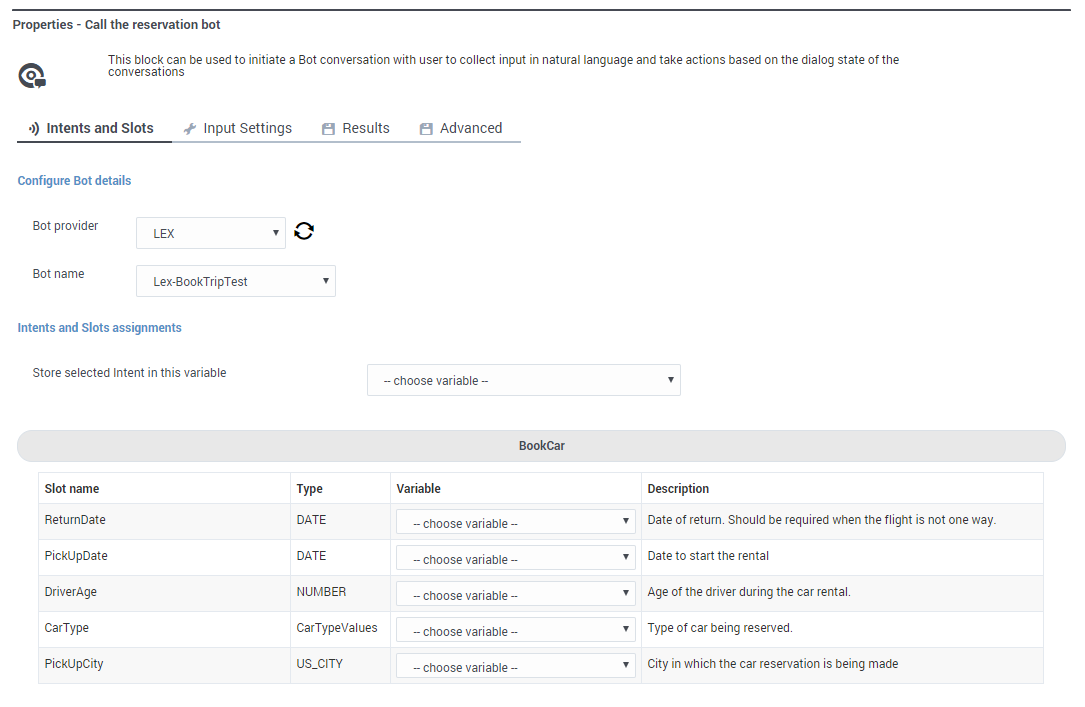
| − | For example, let's say our selected bot resource has an '''Intent''' called " | + | For example, let's say our selected bot resource has an '''Intent''' called "Book Car". The bot detects that the customer wants to reserve a car, but it also needs to know other details about the customer's request, such as the type of vehicle they want, where they are picking it up, and when they plan to return it. The '''Slots''' are used to guide the bot as to the questions it needs to ask the customer (using natural-language) so it can collect this information and thereby fulfill the intent. |
[[File:des_bot_intents_slots.png]] | [[File:des_bot_intents_slots.png]] | ||
| − | + | == Input Settings tab == | |
'''Select Recognition Engine''' | '''Select Recognition Engine''' | ||
| Line 45: | Line 47: | ||
Use these settings to specify how many seconds should elapse before Designer assumes that no voice or chat input has been received from the customer. | Use these settings to specify how many seconds should elapse before Designer assumes that no voice or chat input has been received from the customer. | ||
| − | + | == Results tab == | |
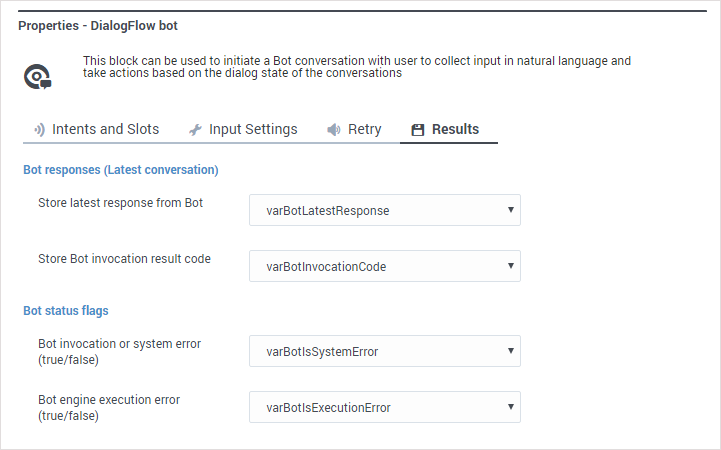
| − | Specify the variables that will hold the bot '''responses''' and '''status flags'''. | + | Specify the variables that will hold the '''bot responses''' and '''status flags''', as returned to the '''Bot''' block from the bot services provider. Each variable is described in more detail below. |
| + | |||
| + | [[File:des_bot_results_tab.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Bot responses === | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Store latest response from bot==== | ||
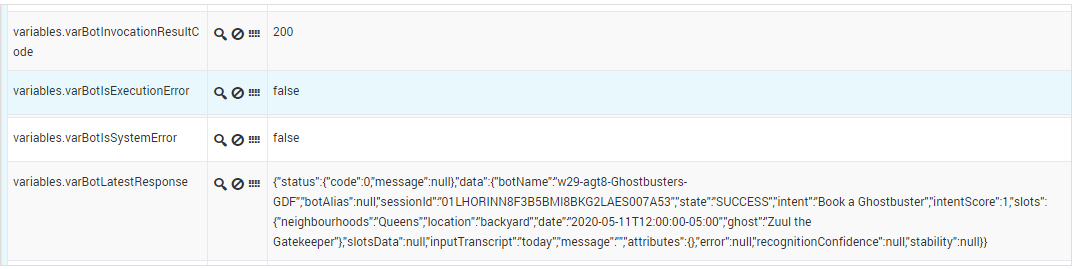
| + | This variable stores details about the latest conversation that the bot engine had with a customer. For example, the results for booking a ghost removal service might look like this (JSON formatted): | ||
| + | |||
| + | <source lang="javascript">{ | ||
| + | "status": { | ||
| + | "code": 0, | ||
| + | "message": null | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "data": { | ||
| + | "botName": "MySampleServiceBookingBot", | ||
| + | "botAlias": null, | ||
| + | "sessionId": "ABC123", | ||
| + | "state": "SUCCESS", | ||
| + | "intent": "Book a Ghostbuster", | ||
| + | "intentScore": 1, | ||
| + | "slots": { | ||
| + | "neighbourhoods": "Queens", | ||
| + | "location": "backyard", | ||
| + | "date": "2020-01-11T12:00:00-05:00", | ||
| + | "ghost": "Zuul the Gatekeeper" | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "slotsData": null, | ||
| + | "inputTranscript": "today", | ||
| + | "message": "", | ||
| + | "attributes": {}, | ||
| + | "error": null, | ||
| + | "recognitionConfidence": null, | ||
| + | "stability": null | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | }</source> | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the example above, some of the details that were returned include: | ||
| + | * <tt>botName</tt> | ||
| + | * <tt>sessionID </tt> | ||
| + | * <tt>state</tt> – indicates SUCCESS if everything worked. | ||
| + | * <tt>intent</tt> – the ''intent'' that was detected (i.e. what the customer wanted to do). | ||
| + | * <tt>slots</tt> – these are the details that the bot collected from the customer to fill the associated ''slots'' (or ''entities'') and fulfill the intent. | ||
| + | * <tt>inputTranscript</tt> – the ''utterance'' (voice or chat input) that the bot received from the customer. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Store bot invocation result code==== | ||
| + | This variable stores the HTTP status code received from the bot when it was last invoked by the application. For example, a result code of <tt>200</tt> (OK) indicates that the bot was successfully invoked. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Any other result code received, such as <tt>401</tt> (Unauthorized) or <tt>403</tt> (Forbidden), can indicate there was a problem reaching the bot service. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Bot status flags === | ||
| + | ====Bot invocation or system error==== | ||
| + | If <tt>true</tt>, this indicates that Designer was not able to successfully reach or invoke the bot service. There could be an issue with the system, or you might need to check the credentials provided for your bot service in the [[SpeechGrammarsBar#Bot_Registry|Bot Registry]]. Otherwise, this returns <tt>false</tt>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Bot engine execution error==== | ||
| + | If <tt>true</tt>, this indicates that Designer was able to communicate with the bot, but an error occurred while the bot engine was processing the request. For example, the bot returned an incorrect response and triggered the '''Error Handler''' block. Otherwise, this returns <tt>false</tt>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Viewing the results data=== | ||
| + | You can view the results data in Designer Analytics by going to the [[SDRDash|Session Data Records dashboard]]. In the '''All Events''' panel, find the application instance you want to check and then filter or search for the data you want to view. | ||
| + | |||
| + | For example: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:des_bot_results_sample.png]] | ||
== Bot Option child blocks == | == Bot Option child blocks == | ||
Revision as of 20:04, July 10, 2020
Contents
Bot Block
Use the Bot block when you want to use a chatbot resource in your application.
Chatbots are software applications that apply automatic speech recognition and natural language understanding to listen and respond to customers in a way that resembles a conversation with a live agent. They have an advantage over Speech Grammars in that they are able to "learn" from each interaction, which means they are always improving their ability to figure out what a customer wants to do without needing that person to provide specific phrases or commands.
For example, they can ask questions and collect information from a customer about setting up a reservation:
Designer bot resources are managed from the Bot Registry, where you can add and manage bot resources from your bot services provider (for a list of supported providers and details about adding bot resources to Designer, see the Bot Registry page). You can use multiple bots in an application, from any of the supported bot services providers.
Typically, you would add a Bot block to the Self Service phase of your application. You can then customize the application logic to specify additional handling, such as call a Shared Module for managing a specific type of intent or send the customer to a live agent for more assistance.
Intents and Slots tab
Use the settings in the Configure Bot details section to select the provider and name of the bot resource you want to use.
Designer then retrieves the details for your bot from the bot services provider and automatically populates the block properties with Intents and Slots. For each Intent, Designer automatically creates an associated child block (similar to how the Menu block creates child blocks for each menu option).
In the Intents and Slots assignment section, you can select the variable that holds the Intent (what does the customer want to do?) and values for the Slots. The Slots (or entities) help provide additional context to the intent.
For example, let's say our selected bot resource has an Intent called "Book Car". The bot detects that the customer wants to reserve a car, but it also needs to know other details about the customer's request, such as the type of vehicle they want, where they are picking it up, and when they plan to return it. The Slots are used to guide the bot as to the questions it needs to ask the customer (using natural-language) so it can collect this information and thereby fulfill the intent.
Input Settings tab
Select Recognition Engine
Select a speech recognition engine to use with this block. Google ASR (Advanced Speech Recognition) is selected by default.
Configure Input Settings
If a speech engine is selected, you can choose to enable the Disable barge-in option. Selecting this option prevents callers from interrupting a prompt while it is still playing. For example, you might want a certain message to play all the way through before the caller can enter another command and skip to the next menu prompt.
If this option is not selected, barge-in is enabled, and the prompt can be interrupted by the caller.
If you don't select a speech engine, you can select the option to play a "beep" sound that will cue the customer for input. You can also set the timeout value to specify how many seconds Designer will wait for input before moving on to the next step in processing.
Input timeout
Use these settings to specify how many seconds should elapse before Designer assumes that no voice or chat input has been received from the customer.
Results tab
Specify the variables that will hold the bot responses and status flags, as returned to the Bot block from the bot services provider. Each variable is described in more detail below.
Bot responses
Store latest response from bot
This variable stores details about the latest conversation that the bot engine had with a customer. For example, the results for booking a ghost removal service might look like this (JSON formatted):
{
"status": {
"code": 0,
"message": null
},
"data": {
"botName": "MySampleServiceBookingBot",
"botAlias": null,
"sessionId": "ABC123",
"state": "SUCCESS",
"intent": "Book a Ghostbuster",
"intentScore": 1,
"slots": {
"neighbourhoods": "Queens",
"location": "backyard",
"date": "2020-01-11T12:00:00-05:00",
"ghost": "Zuul the Gatekeeper"
},
"slotsData": null,
"inputTranscript": "today",
"message": "",
"attributes": {},
"error": null,
"recognitionConfidence": null,
"stability": null
}
}In the example above, some of the details that were returned include:
- botName
- sessionID
- state – indicates SUCCESS if everything worked.
- intent – the intent that was detected (i.e. what the customer wanted to do).
- slots – these are the details that the bot collected from the customer to fill the associated slots (or entities) and fulfill the intent.
- inputTranscript – the utterance (voice or chat input) that the bot received from the customer.
Store bot invocation result code
This variable stores the HTTP status code received from the bot when it was last invoked by the application. For example, a result code of 200 (OK) indicates that the bot was successfully invoked.
Any other result code received, such as 401 (Unauthorized) or 403 (Forbidden), can indicate there was a problem reaching the bot service.
Bot status flags
Bot invocation or system error
If true, this indicates that Designer was not able to successfully reach or invoke the bot service. There could be an issue with the system, or you might need to check the credentials provided for your bot service in the Bot Registry. Otherwise, this returns false.
Bot engine execution error
If true, this indicates that Designer was able to communicate with the bot, but an error occurred while the bot engine was processing the request. For example, the bot returned an incorrect response and triggered the Error Handler block. Otherwise, this returns false.
Viewing the results data
You can view the results data in Designer Analytics by going to the Session Data Records dashboard. In the All Events panel, find the application instance you want to check and then filter or search for the data you want to view.
For example:
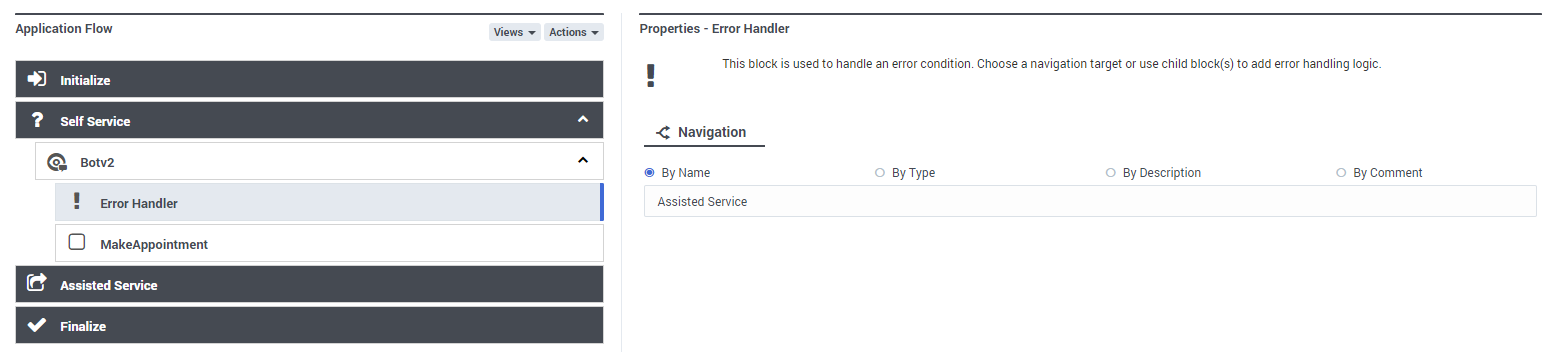
Bot Option child blocks
Additional Bot Option child blocks for each intent are also created, along with an Error Handler block. For each Intent, you can go to its related Bot Option child-block to edit its label and give it a more meaningful name.
In the properties for the Error Handler block, you can specify the action to take if an error occurs (for example, go to another block or the Assisted Service phase):