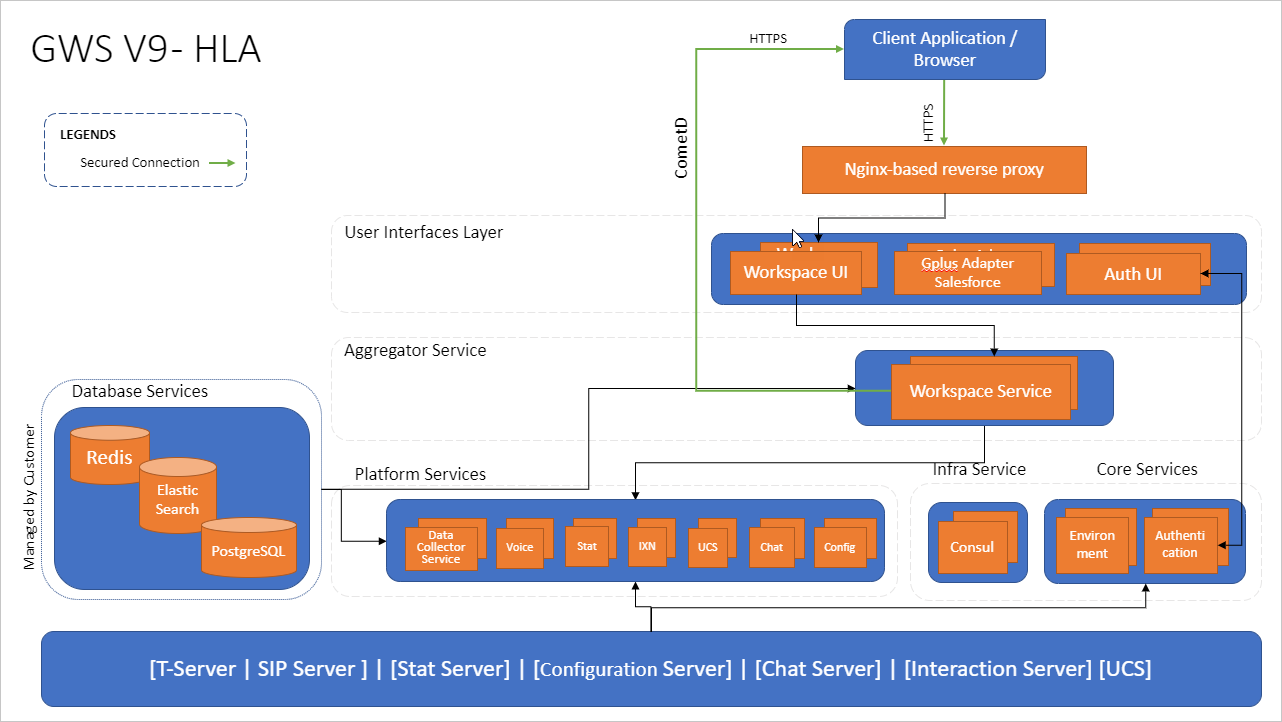
Architecture of Web Services and Applications
Description of the preceding diagram
Genesys Web Services (GWS) is an application cluster composed of several microservices that run together. GWS runs on multiple containers that are categorized as below:
- Data Services: These services use multiple data sources (third-party databases) that you must maintain to store GWS data.
- Platform Services: These services are used to connect to Genesys servers such as Configuration Server, Stat Server, SIP Server, and Interaction Server.
- Core Services: These services are used for Web Services and Applications configuration and authentication.
- UI Services: These services provide user interfaces (Workspace Web Edition and the authentication UI) and the underlying services needed to support them, such as the Workspace Service.
- Client Application/Browser: This can be Workspace Web Edition Agent Desktop, a custom desktop or Gplus Adapter for Salesforce.
A reverse proxy service is used as an ingress controller. This works as an internal application load balancer.
Data Storage Sources
GWS v9 uses multiple data sources to store its data.
PostgreSQL
- PostgreSQL is used to store GWS-specific configuration details (contact center and environment).
- Data stored in PostgreSQL is persistent.
Redis
- Redis is used for system-wide caching, where concurrent requests are served from cache.
- Data stored in Redis is not persistent. It is always runtime.
Elasticsearch
- Elasticsearch provides searchable data from Configuration Server, which is used by Workspace Web Edition and other services.
- Elasticsearch is used to store statistical information for Workspace Web Edition functionality.
- Data stored in Elasticsearch is not persistent. It is always runtime.
CometD
Web Services uses CometD version 3, an HTTP-based routing bus that uses an Ajax Push technology pattern known as Comet. Comet is a web application model that allows an HTTP request to push data to a browser, even if the browser has not requested it.
Web Services uses CometD to deliver unsolicited notifications to clients for real-time events, such as getting a new call or chat message. At runtime, CometD delivers messages, providing clients with a consistent approach while maintaining support for multiple browsers.
For details about CometD, see http://cometd.org/.