Contents
Controlling User Access
You can limit user access and activities in the Callback application to what is appropriate for each user's role in your enterprise. For example, to perform their duties, it is sufficient for some users to only view the list of callback records in the Callback application, without the ability to modify a callback in any way. Other users might require additional permissions; for example, some users might require access permissions that allow them to view errors associated with callbacks so they can troubleshoot problems.
You configure the restrictions on user access and activities for Callback in the Platform Administration application. If you do not configure access and activity restrictions for a user, then that user has full access to everything in the Callback application.
Genesys provides predefined Roles for the Callback application to ensure that your users have access that is appropriate for your business needs – such as the ability to view and modify Callbacks, use the Developer tab, and view Callbacks based on lines of business. For detailed information about Roles, see the Roles section in the Platform Administration documentation.
Migration of Roles
If you have not yet moved to the Roles and Access Group settings described on this page, the original method for configuring Callback access still applies to your setup. In the original configuration, Callback access was granted when the ges or gms section in the Person object's annex included a role option (for example, Administrator).
To move to the new configuration method for granting access, add your user to the correct Callback or custom Access Group and remove the ges or gms section. If you don't remove the ges or gms section, the old configuration applies and the Access Group is not taken into consideration.
Callback Roles
Genesys provides the following default Callback Roles:
- Callback Administrator—Callback Administrators have full access to the Callback application, which includes the ability to create, cancel, and reschedule callbacks, and to export reports. Users with this Role can also access all of the Developer tab features.
- Callback Supervisor—Supervisor users have full access to the Callback panel, which includes the ability to create, cancel, and reschedule callbacks, and export reports. They cannot access the Developer tab in the Callback application.
- Callback Monitor—Monitor users can only view callbacks.
- Callback Developer—Developer users can view callbacks on the Callback tab and have full access to the Developer tab, which includes the ability to view recent errors, test API keys, and to provision Callback.
If a user is a member of more than one Role, the Role that allows the most access to Callback features takes precedence.
Predefined Access Groups Supporting Callback
By default, Genesys defines a list of Access Groups and adds Callback Roles to some of these groups, as described below. Users who are already in these Access Groups are given Callback permissions by default. For example, any user in your Administrators Access Group is automatically granted the Callback Administrator role.
| Access Group | Callback Administrator Role | Callback Supervisor Role | Callback Monitor Role | Callback Developer Role |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Administrators | ✓ | |||
| Supervisors | ✓ | |||
| Managers | ✓ | |||
| Callback Developers | ✓ |
Line of Business Segmentation
By default, all users who are part of standard Access Groups and can access the Callback application will have Read permission for all the Virtual Queues. To restrict access to queues based on your lines of business, you can create custom Access Groups and enable or disable Read permissions as required.
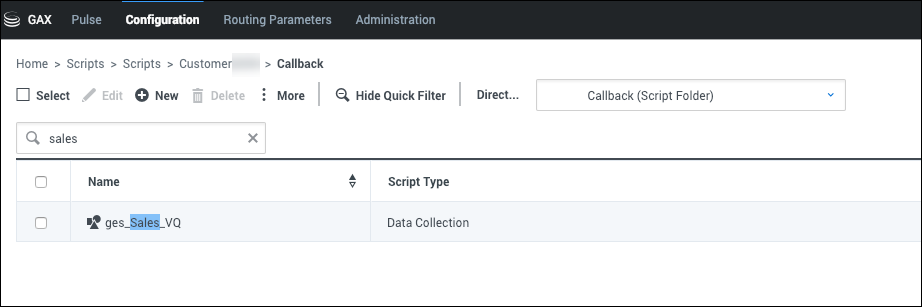
Any time you provision a Virtual Queue in Designer's CALLBACK_SETTINGS data table, the Callback service automatically creates a Script object in Platform Administration > Scripts > Callback. The created Script object has the same name as the Virtual Queue and is prefixed with the ges_ label. For example, if you create a Virtual Queue called Sales_VQ, there will be a Script object called ges_Sales_VQ in the Callback directory.
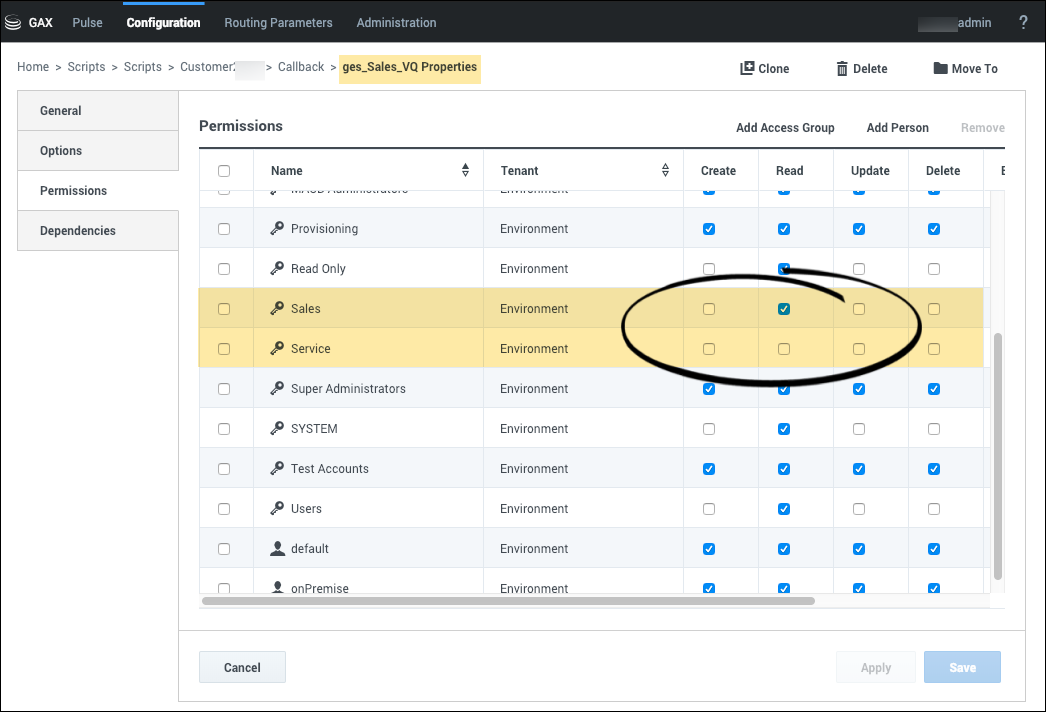
To control access to queues based on your lines of business, you must create Access Groups for your various lines of business and then enable or disable access to the script objects that represent the virtual queues for each group. For a user to access a specific queue, the Access Group to which the user belongs must have the Read permission for the script object that represents that queue. The Read permission is assigned by default to all Access Groups, which means that all Access Groups can access all Virtual Queues until you change the permissions. To deny access to a Virtual Queue, navigate to the Script object associated with the queue and remove the Read permission from Access Groups that do not require access to that queue.
For example, if your Tenant has two lines of business called Sales and Service, you could create two Access Groups for Callback: Sales and Service. Then, navigate to the script object representing the VQ and add that Access Group with read permission:
- In the ges_Sales_VQ Script object, retain the Read access for the Sales team and disable the Read permission for the Service team.
- In the ges_Service_VQ Script object, retain the Read access for the Service team and remove the Read permission from the Sales team.
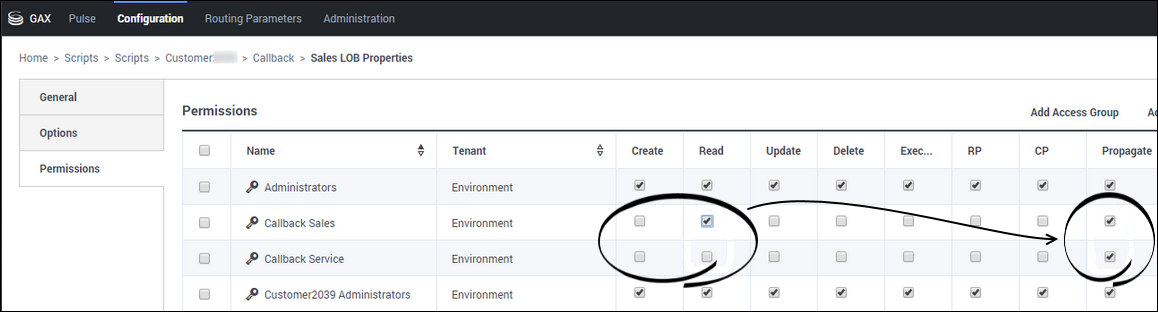
To set permissions on groups of Virtual Queues (instead of one at a time), create subfolders under the Scripts > Callback folder and apply appropriate permissions to the subfolder. Then, move the Script objects representing the various Virtual Queues into the corresponding subfolder. Any Script object that is in a subfolder will inherit the permissions of that subfolder. Check the Propagate box to apply the permissions to any object that is in the folder. The permissions apply to any Virtual Queue that is in the subfolder now and will apply to any new Virtual Queue that you add to the subfolder in the future.